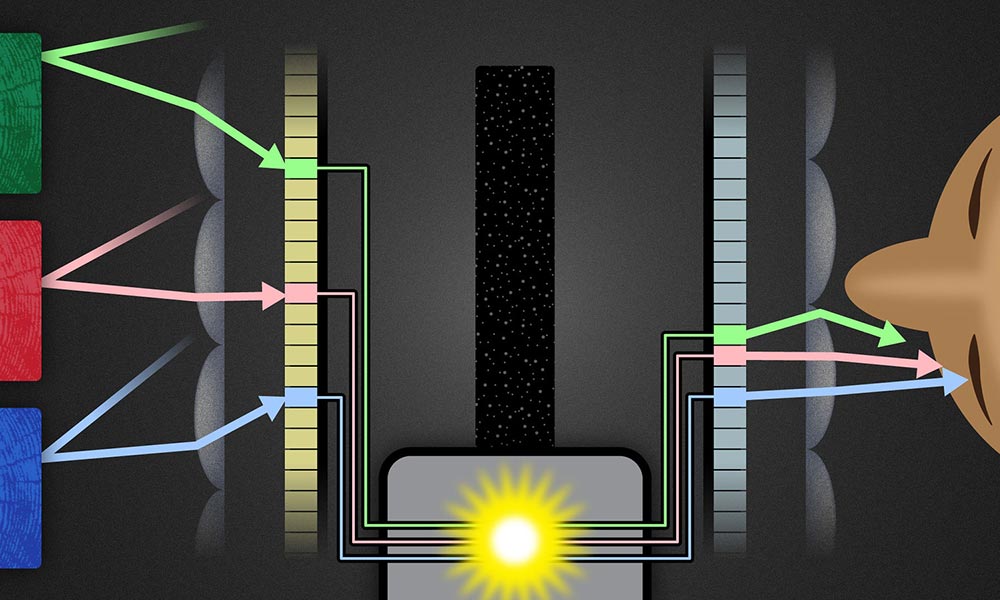
Society & Culture
Come on baby, (re)light my fire
July 20, 2016
New research indicates that there are ways that couples can sustain—or relight—their passion. The study suggests that when men and women perceive their partners as responsive, they feel special and think of their partner as a valuable mate, which in turn boosts sexual desirability.