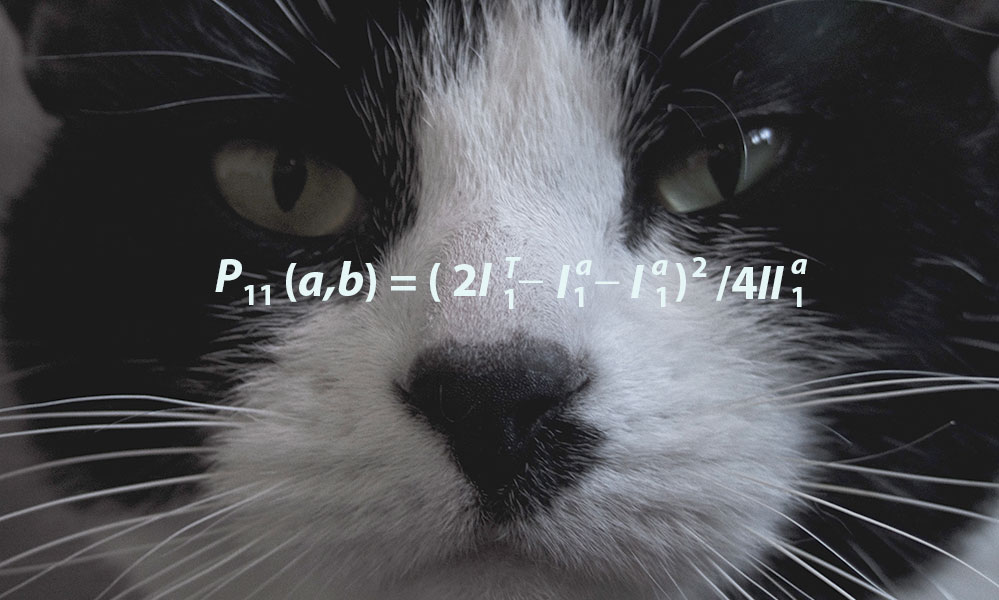Society & Culture
Data mining Instagram feeds can point to teenage drinking patterns
October 29, 2015
By extracting information from Instagram images and hashtags, computer science researchers have shown they can expose patterns of underage drinking more cheaply and faster than conventional surveys.