Science & Technology
Doing more with less: New technique efficiently finds quantum wave functions
August 28, 2014
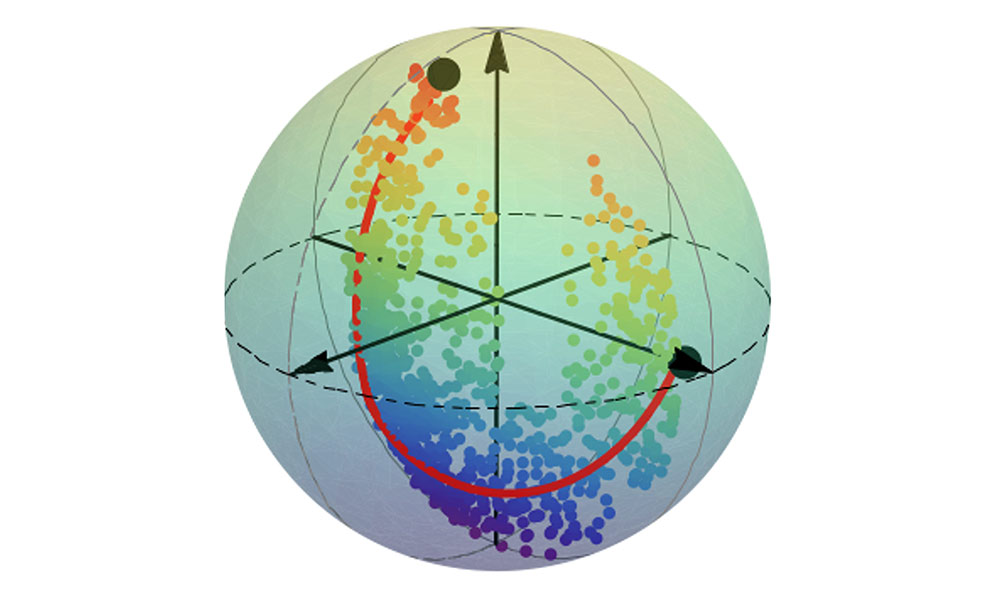
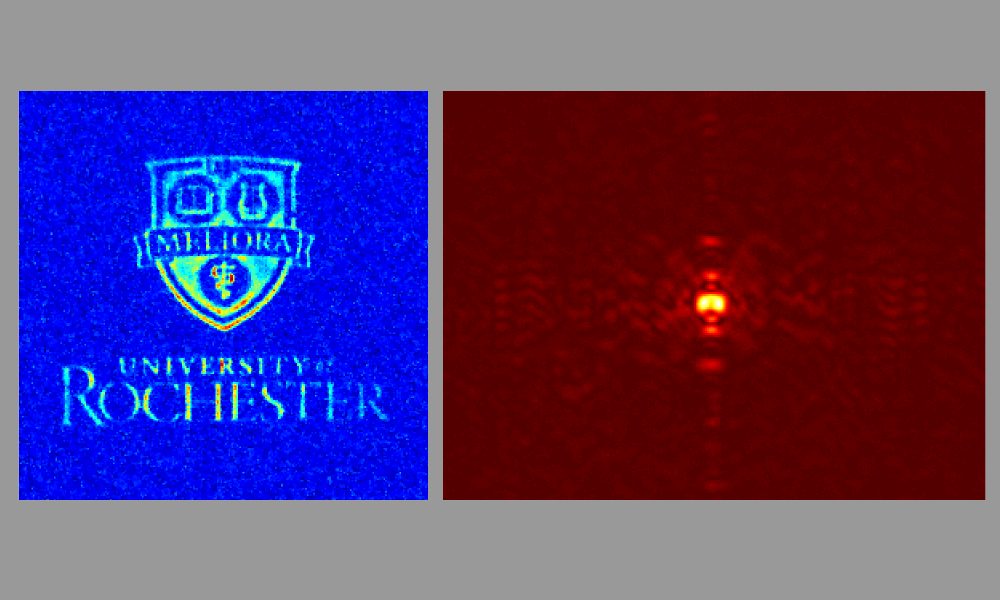
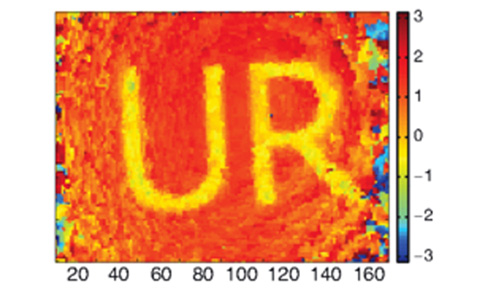
University researchers have introduced a new method, called compressive direct measurement, that allowed the team to reconstruct a quantum state at 90 percent fidelity using only a quarter of the measurements required by previous methods.